The UNIQUE function is a life saver function that selects unique data from your dataset or a specified range, array, effectively helping to minimize redundancy in data sets.
Syntax
The syntax of the UNIQUE function is straightforward:
UNIQUE(array, [by_col], [exactly_once])– array: The range or array from which to extract unique values.
– by_col: (Optional) A boolean value indicating whether to compare by column (TRUE) or by row (FALSE).
– exactly_once: (Optional) A boolean value to return unique values that occur exactly once if set to TRUE.
Examples
Example 1: Basic Use
To extract unique values from a single column of data in cells A1:A5, use the following formula:
=UNIQUE(A1:A5)If the range contains the values (A, B, B, C, C), the result will be: A, B, C.
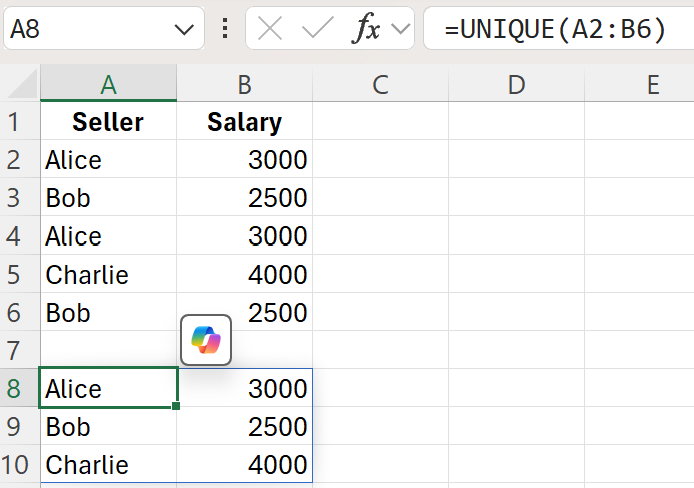
Example 2: Extracting Unique Records from Multiple Columns
To get unique combinations of values from two columns, say A2:B6, you would use:
=UNIQUE(A2:B6)This will return a list of unique row combinations from the specified range.
Example 3: Unique Values that Occur Exactly Once
To return only those unique values that appear exactly once within the range A2:B6, you can set the last argument to TRUE:
=UNIQUE(A1:A5, FALSE, TRUE)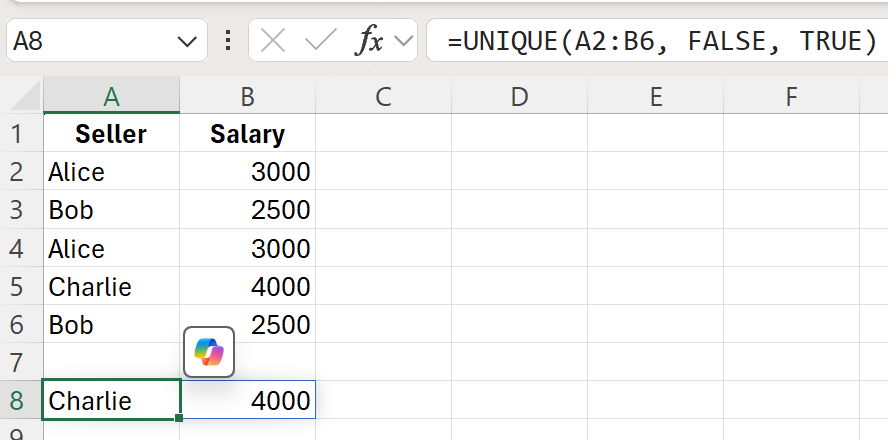
Error Handling
Errors may arise while using the UNIQUE function. Here are some common ones to be aware of:
– N/A: This error can occur if the array specified is invalid or empty. Make sure your range is correctly defined.
– VALUE!: This might happen if the function arguments are not compatible, especially when using the optional parameters.
Being mindful of these potential issues will streamline your experience when working with the UNIQUE function.
Conclusion
The UNIQUE function is an essential tool for anyone who needs to analyze or manipulate data within Excel. By allowing users to effortlessly extract unique values from various ranges, it simplifies the process of data analysis and improves accuracy. Leveraging this function can lead to better insights and more effective data management.
Related Articles
If you would like to see UNIQUE function being used in the combination of SUM, then see my other article here.
